title
stringlengths 30
170
| detail_url
stringlengths 45
45
| author_list
sequencelengths 2
28
| abstract
stringlengths 403
403
|
|---|---|---|---|
Staging energy sources to extend flight time of a multirotor UAV | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341804/ | [
"Karan P. Jain",
"Jerry Tang",
"Koushil Sreenath",
"Mark W. Mueller",
"Karan P. Jain",
"Jerry Tang",
"Koushil Sreenath",
"Mark W. Mueller"
] | Energy sources such as batteries do not decrease in mass after consumption, unlike combustion-based fuels. We present the concept of staging energy sources, i.e. consuming energy in stages and ejecting used stages, to progressively reduce the mass of aerial vehicles in-flight which reduces power consumption, and consequently increases flight time. A flight time vs. energy storage mass analysis is ... |
UAV-AdNet: Unsupervised Anomaly Detection using Deep Neural Networks for Aerial Surveillance | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341790/ | [
"Ilker Bozcan",
"Erdal Kayacan",
"Ilker Bozcan",
"Erdal Kayacan"
] | Anomaly detection is a key goal of autonomous surveillance systems that should be able to alert unusual observations. In this paper, we propose a holistic anomaly detection system using deep neural networks for surveillance of critical infrastructures (e.g., airports, harbors, warehouses) using an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). First, we present a heuristic method for the explicit representation o... |
ROSflight: A Lean Open-Source Research Autopilot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341653/ | [
"James Jackson",
"Daniel Koch",
"Trey Henrichsen",
"Tim McLain",
"James Jackson",
"Daniel Koch",
"Trey Henrichsen",
"Tim McLain"
] | ROSflight is a lean, open-source autopilot system developed with the primary goal of supporting the needs of researchers working with micro aerial vehicle systems. The project consists of firmware designed to run on low-cost, readily available flight controller boards, as well as ROS packages for interfacing between the flight controller and application code and for simulation. The core objectives... |
Online Weight-adaptive Nonlinear Model Predictive Control | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341495/ | [
"Dimche Kostadinov",
"Davide Scaramuzza",
"Dimche Kostadinov",
"Davide Scaramuzza"
] | Nonlinear Model Predictive Control (NMPC) is a powerful and widely used technique for nonlinear dynamic process control under constraints. In NMPC, the state and control weights of the corresponding state and control costs are commonly selected based on human-expert knowledge, which usually reflects the acceptable stability in practice. Although broadly used, this approach might not be optimal for... |
CinemAirSim: A Camera-Realistic Robotics Simulator for Cinematographic Purposes | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341066/ | [
"Pablo Pueyo",
"Eric Cristofalo",
"Eduardo Montijano",
"Mac Schwager",
"Pablo Pueyo",
"Eric Cristofalo",
"Eduardo Montijano",
"Mac Schwager"
] | Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are becoming increasingly popular in the film and entertainment industries, in part because of their maneuverability and perspectives they enable. While there exists methods for controlling the position and orientation of the drones for visibility, other artistic elements of the filming process, such as focal blur, remain unexplored in the robotics community. The la... |
Design and Evaluation of a Perching Hexacopter Drone for Energy Harvesting from Power Lines | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341100/ | [
"Ryan Kitchen",
"Nick Bierwolf",
"Sean Harbertson",
"Brage Platt",
"Dean Owen",
"Klaus Griessmann",
"Mark A. Minor",
"Ryan Kitchen",
"Nick Bierwolf",
"Sean Harbertson",
"Brage Platt",
"Dean Owen",
"Klaus Griessmann",
"Mark A. Minor"
] | With a growing number of applications in the world for UAVs, there is a clear limitation regarding the need for extended battery life. With the current flight times, many users would benefit greatly with an innovative option of field charging these devices. The objective of this project is to investigate feasibility of inductively harvesting energy from a power line cable for applications such as ... |
SplitFlyer: a Modular Quadcoptor that Disassembles into Two Flying Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340797/ | [
"Songnan Bai",
"Shixin Tan",
"Pakpong Chirarattananon",
"Songnan Bai",
"Shixin Tan",
"Pakpong Chirarattananon"
] | We introduce SplitFlyer-a novel quadcopter with an ability to disassemble into two self-contained bicopters through human assistance. As a subunit, the bicopter is a severely underactuated aerial vehicle equipped with only two propellers. Still, each bicopter is capable of independent flight. To achieve this, we provide an analysis of the system dynamics by relaxing the control over the yaw rotati... |
Towards Cooperative Transport of a Suspended Payload via Two Aerial Robots with Inertial Sensing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341670/ | [
"Heng Xie",
"Xinyu Cai",
"Pakpong Chirarattananon",
"Heng Xie",
"Xinyu Cai",
"Pakpong Chirarattananon"
] | This paper addresses the problem of cooperative transport of a point mass hoisted by two aerial robots. Treating the robots as a leader and a follower, the follower stabilizes the system with respect to the leader using only feedback from its Inertial Measurement Units (IMU). This is accomplished by neglecting the acceleration of the leader, analyzing the system through the generalized coordinates... |
Toward Enabling a Hundred Drones to Land in a Minute | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341360/ | [
"Daiki Fujikura",
"Kenjiro Tadakuma",
"Masahiro Watanabe",
"Yoshito Okada",
"Kazunori Ohno",
"Satoshi Tadokoro",
"Daiki Fujikura",
"Kenjiro Tadakuma",
"Masahiro Watanabe",
"Yoshito Okada",
"Kazunori Ohno",
"Satoshi Tadokoro"
] | Currently, drone research and development has received significant attention worldwide. Particularly, delivery services employ drones as it is a viable method to improve delivery efficiency by using a several unmanned drones. Research has been conducted to realize complete automation of drone control for such services. However, regarding the takeoff and landing port of the drones, conventional met... |
Wind and the City: Utilizing UAV-Based In-Situ Measurements for Estimating Urban Wind Fields | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340812/ | [
"Jay Patrikar",
"Brady G. Moon",
"Sebastian Scherer",
"Jay Patrikar",
"Brady G. Moon",
"Sebastian Scherer"
] | A high-quality estimate of wind fields can potentially improve the safety and performance of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) operating in dense urban areas. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations can help provide a wind field estimate, but their accuracy depends on the knowledge of the distribution of the inlet boundary conditions. This paper provides a real-time methodology using a Partic... |
Microdrone-Equipped Mobile Crawler Robot System, DIR-3, for High-Step Climbing and High-Place Inspection | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340972/ | [
"Yuji OGUSU",
"Kohji TOMITA",
"Akiya KAMIMURA",
"Yuji OGUSU",
"Kohji TOMITA",
"Akiya KAMIMURA"
] | Mobile robots of various types have been proposed for infrastructure inspection and disaster investigation. For such mobile robot applications, accessing the areas is of primary importance for missions. Therefore, various locomotive mechanisms have been studied. We introduce a novel mobile robot system, named DIR-3, combining a crawler robot and a microdrone. By rotating its arm back and forth, DI... |
MHYRO: Modular HYbrid RObot for contact inspection and maintenance in oil & gas plants | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341639/ | [
"A. Lopez-Lora",
"P.J. Sanchez-Cuevas",
"A. Suarez",
"A. Garofano-Soldado",
"A. Ollero",
"G. Heredia",
"A. Lopez-Lora",
"P.J. Sanchez-Cuevas",
"A. Suarez",
"A. Garofano-Soldado",
"A. Ollero",
"G. Heredia"
] | In this paper, we propose a new concept of robot which is hybrid, including aerial and crawling subsystems and an arm, and also modular with interchangeable crawling subsystems for different pipe configurations, since it has been designed to cover most industrial oil & gas end-users' requirements. The robot has the same ability than aerial robots to reach otherwise inaccessible locations, but make... |
Geomorphological Analysis Using Unpiloted Aircraft Systems, Structure from Motion, and Deep Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341354/ | [
"Zhiang Chen",
"Tyler R. Scott",
"Sarah Bearman",
"Harish Anand",
"Devin Keating",
"Chelsea Scott",
"J Ramón Arrowsmith",
"Jnaneshwar Das",
"Zhiang Chen",
"Tyler R. Scott",
"Sarah Bearman",
"Harish Anand",
"Devin Keating",
"Chelsea Scott",
"J Ramón Arrowsmith",
"Jnaneshwar Das"
] | We present a pipeline for geomorphological analysis that uses structure from motion (SfM) and deep learning on close-range aerial imagery to estimate spatial distributions of rock traits (size, roundness, and orientation) along a tectonic fault scarp. The properties of the rocks on the fault scarp derive from the combination of initial volcanic fracturing and subsequent tectonic and geomorphic fra... |
In-flight Efficient Controller Auto-tuning using a Pair of UAVs | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341025/ | [
"Wojciech Giernacki",
"Dariusz Horla",
"Martin Saska",
"Wojciech Giernacki",
"Dariusz Horla",
"Martin Saska"
] | In the paper, a pair of auto-tuning methods for fixed-parameter controllers is presented, in application to multirotor unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) control. In both cases, the automatized process of searching the best altitude controller parameters is carried out with the use of a modified golden-search method, for a selected cost function, during the flight of a pair of UAVs. All the calculati... |
A Novel Trajectory Optimization for Affine Systems: Beyond Convex-Concave Procedure | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341566/ | [
"Fatemeh Rastgar",
"Arun Kumar Singh",
"Houman Masnavi",
"Karl Kruusamae",
"Alvo Aabloo",
"Fatemeh Rastgar",
"Arun Kumar Singh",
"Houman Masnavi",
"Karl Kruusamae",
"Alvo Aabloo"
] | Trajectory optimization problems under affine motion model and convex cost function are often solved through the convex-concave procedure (CCP), wherein the non-convex collision avoidance constraints are replaced with its affine approximation. Although mathematically rigorous, CCP has some critical limitations. First, it requires a collision-free initial guess of solution trajectory which is diffi... |
Development of A Passive Skid for Multicopter Landing on Rough Terrain | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340906/ | [
"Maozheng Xu",
"Naoto Sumida",
"Takeshi Takaki",
"Maozheng Xu",
"Naoto Sumida",
"Takeshi Takaki"
] | Landing is an essential part of multicopter task operations. A multicopter has relatively stringent requirements for landing, particularly for achieving flatness. Currently, landing on rough terrain with normal skids is difficult. Therefore, research is being conducted to obtain skids capable of landing on rough terrain. In this paper, a passive skid for multicopter landing on rough terrain is pro... |
Template-Based Optimal Robot Design with Application to Passive-Dynamic Underactuated Flapping | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341125/ | [
"Avik De",
"Robert J. Wood",
"Avik De",
"Robert J. Wood"
] | We present a novel paradigm and algorithm for optimal design of underactuated robot platforms in highly-constrained nonconvex parameter spaces. We apply this algorithm to two variants of the mature RoboBee platform, numerically demonstrating predicted performance improvements of over 10% in some cases by algorithmically reasoning about variable effective-mechanical-advantage (EMA) transmissions, h... |
A Whisker-inspired Fin Sensor for Multi-directional Airflow Sensing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341723/ | [
"Suhan Kim",
"Regan Kubicek",
"Aleix Paris",
"Andrea Tagliabue",
"Jonathan P. How",
"Sarah Bergbreiter",
"Suhan Kim",
"Regan Kubicek",
"Aleix Paris",
"Andrea Tagliabue",
"Jonathan P. How",
"Sarah Bergbreiter"
] | This work presents the design, fabrication, and characterization of an airflow sensor inspired by the whiskers of animals. The body of the whisker was replaced with a fin structure in order to increase the air resistance. The fin was suspended by a micro-fabricated spring system at the bottom. A permanent magnet was attached beneath the spring, and the motion of fin was captured by a readily acces... |
PufferBot: Actuated Expandable Structures for Aerial Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341088/ | [
"Hooman Hedayati",
"Ryo Suzuki",
"Daniel Leithinger",
"Daniel Szafir",
"Hooman Hedayati",
"Ryo Suzuki",
"Daniel Leithinger",
"Daniel Szafir"
] | We present PufferBot, an aerial robot with an expandable structure that may expand to protect a drone's propellers when the robot is close to obstacles or collocated humans. PufferBot is made of a custom 3D-printed expandable scissor structure, which utilizes a one degree of freedom actuator with rack and pinion mechanism. We propose four designs for the expandable structure, each with unique char... |
Optimal-power Configurations for Hover Solutions in Mono-spinners | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341648/ | [
"Mojtaba Hedayatpour",
"Mehran Mehrandezh",
"Farrokh Janabi-Sharifi",
"Mojtaba Hedayatpour",
"Mehran Mehrandezh",
"Farrokh Janabi-Sharifi"
] | Rotary-wing flying machines draw attention within the UAV community for their in-place hovering capability, and recently, holonomic motion over fixed-wings. In this paper, we investigate about the power-optimality in a mono-spinner, i.e., a class of rotary-wing UAVs with one rotor only, whose main body has a streamlined shape for producing additional lift when counter-spinning the rotor. We provid... |
Flight Control of Sliding Arm Quadcopter with Dynamic Structural Parameters | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340694/ | [
"Rumit Kumar",
"Aditya M. Deshpande",
"James Z. Wells",
"Manish Kumar",
"Rumit Kumar",
"Aditya M. Deshpande",
"James Z. Wells",
"Manish Kumar"
] | The conceptual design and flight controller of a novel kind of quadcopter are presented. This design is capable of morphing the shape of the UAV during flight to achieve position and attitude control. We consider a dynamic center of gravity (CoG) which causes continuous variation in a moment of inertia (MoI) parameters of the UAV. These dynamic structural parameters play a vital role in the stabil... |
Design and Control of SQUEEZE: A Spring-augmented QUadrotor for intEractions with the Environment to squeeZE-and-fly | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341730/ | [
"Karishma Patnaik",
"Shatadal Mishra",
"Seyed Mostafa Rezayat Sorkhabadi",
"Wenlong Zhang",
"Karishma Patnaik",
"Shatadal Mishra",
"Seyed Mostafa Rezayat Sorkhabadi",
"Wenlong Zhang"
] | This paper presents the design and control of a novel quadrotor with a variable geometry to physically interact with cluttered environments and fly through narrow gaps and passageways. This compliant quadrotor with passive morphing capabilities is designed using torsional springs at every arm hinge to allow for rotation driven by external forces. We derive the dynamic model of this variable geomet... |
Hybrid aerial-ground locomotion with a single passive wheel | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341577/ | [
"Youming Qin",
"Yihang Li",
"Xu Wei",
"Fu Zhang",
"Youming Qin",
"Yihang Li",
"Xu Wei",
"Fu Zhang"
] | Exploiting contacts with environment structures provides extra force support to a UAV, often reducing the power consumption and hence extending the mission time. This paper investigates one such way to exploit flat surfaces in the environment by a novel aerial-ground hybrid locomotion. Our design is a single passive wheel integrated at the UAV bottom, serving a minimal design to date. We present t... |
Adaptive Nonlinear Control For Perching of a Bioinspired Ornithopter | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341793/ | [
"F. J. Maldonado",
"J. Á. Acosta",
"J. Tormo-Barbero",
"P. Grau",
"M. M. Guzmán",
"A. Ollero",
"F. J. Maldonado",
"J. Á. Acosta",
"J. Tormo-Barbero",
"P. Grau",
"M. M. Guzmán",
"A. Ollero"
] | This work presents a model-free nonlinear controller for an ornithopter prototype with bioinspired wings and tail. The size and power requirements have been thought to allocate a customized autopilot on board. To assess the functionality and performance of the full mechatronic design, a controller has been designed and implemented to execute a prescribed perching 2D trajectory. Although functional... |
A collision-resilient aerial vehicle with icosahedron tensegrity structure | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341236/ | [
"Jiaming Zha",
"Xiangyu Wu",
"Joseph Kroeger",
"Natalia Perez",
"Mark W. Mueller",
"Jiaming Zha",
"Xiangyu Wu",
"Joseph Kroeger",
"Natalia Perez",
"Mark W. Mueller"
] | Aerial vehicles with collision resilience can operate with more confidence in environments with obstacles that are hard to detect and avoid. This paper presents the methodology used to design a collision resilient aerial vehicle with icosahedron tensegrity structure. A simplified stress analysis of the tensegrity frame under impact forces is performed to guide the selection of its components. In a... |
Experimental flights of adaptive patterns for cloud exploration with UAVs | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341408/ | [
"Titouan Verdu",
"Nicolas Maury",
"Pierre Narvor",
"Florian Seguin",
"Gregory Roberts",
"Fleur Couvreux",
"Grégoire Cayez",
"Murat Bronz",
"Gautier Hattenberger",
"Simon Lacroix",
"Titouan Verdu",
"Nicolas Maury",
"Pierre Narvor",
"Florian Seguin",
"Gregory Roberts",
"Fleur Couvreux",
"Grégoire Cayez",
"Murat Bronz",
"Gautier Hattenberger",
"Simon Lacroix"
] | This work presents the deployment of UAVs for the exploration of clouds, from the system architecture and simulation tests to a real-flight campaign and trajectory analyzes. Thanks to their small size and low altitude, light UAVs have proven to be adapted for in-situ cloud data collection. The short life time of the clouds and limited endurance of the planes require to focus on the area of maximum... |
Navigation-Assistant Path Planning within a MAV team | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340792/ | [
"Youngseok Jang",
"Yunwoo Lee",
"H. Jin Kim",
"Youngseok Jang",
"Yunwoo Lee",
"H. Jin Kim"
] | In micro aerial vehicle (MAV) operations, the success of a mission is highly dependent on navigation performance, which has raised recent interests on navigation-aware path planning. One of the challenges lies in that optimal motions for successful navigation and the designated mission are often different in unknown, unstructured environments, and only sub-optimality may be obtained in each aspect... |
UAV Coverage Path Planning under Varying Power Constraints using Deep Reinforcement Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340934/ | [
"Mirco Theile",
"Harald Bayerlein",
"Richard Nai",
"David Gesbert",
"Marco Caccamo",
"Mirco Theile",
"Harald Bayerlein",
"Richard Nai",
"David Gesbert",
"Marco Caccamo"
] | Coverage path planning (CPP) is the task of designing a trajectory that enables a mobile agent to travel over every point of an area of interest. We propose a new method to control an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) carrying a camera on a CPP mission with random start positions and multiple options for landing positions in an environment containing no-fly zones. While numerous approaches have been p... |
Detection-Aware Trajectory Generation for a Drone Cinematographer | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341368/ | [
"Boseong Felipe Jeon",
"Dongsuk Shim",
"H. Jin Kim",
"Boseong Felipe Jeon",
"Dongsuk Shim",
"H. Jin Kim"
] | This work investigates an efficient trajectory generation for chasing a dynamic target, which incorporates the detectability objective. The proposed method actively guides the motion of a cinematographer drone so that the color of a target is well-distinguished against the colors of the background in the view of the drone. For the objective, we define a measure of color detectability given a chasi... |
Motion Planning for Heterogeneous Unmanned Systems under Partial Observation from UAV | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341326/ | [
"Ci Chen",
"Yuanfang Wan",
"Baowei Li",
"Chen Wang",
"Guangming Xie",
"Huanyu Jiang",
"Ci Chen",
"Yuanfang Wan",
"Baowei Li",
"Chen Wang",
"Guangming Xie",
"Huanyu Jiang"
] | For heterogeneous unmanned systems composed of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs), using UAVs serve as eyes to assist UGVs in motion planning is a promising research direction due to the UAVs' vast view scope. However, its limitations on flight altitude prevent the UAVs from observing the global map. Thus motion planning in the local map becomes a Partially Observa... |
Multi-UAV Coverage Path Planning for the Inspection of Large and Complex Structures | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341089/ | [
"Wei Jing",
"Di Deng",
"Yan Wu",
"Kenji Shimada",
"Wei Jing",
"Di Deng",
"Yan Wu",
"Kenji Shimada"
] | We present a multi-UAV Coverage Path Planning (CPP) framework for the inspection of large-scale, complex 3D structures. In the proposed sampling-based coverage path planning method, we formulate the multi-UAV inspection applications as a multi-agent coverage path planning problem. By combining two NP-hard problems: Set Covering Problem (SCP) and Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP), a Set-Covering Vehicl... |
Generating Minimum-Snap Quadrotor Trajectories Really Fast | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341794/ | [
"Declan Burke",
"Airlie Chapman",
"Iman Shames",
"Declan Burke",
"Airlie Chapman",
"Iman Shames"
] | We propose an algorithm for generating minimum-snap trajectories for quadrotors with linear computational complexity with respect to the number of segments in the spline trajectory. Our algorithm is numerically stable for large numbers of segments and is able to generate trajectories of more than 500, 000 segments. The computational speed and numerical stability of our algorithm makes it suitable ... |
Persistent Connected Power Constrained Surveillance with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341662/ | [
"Pradipta Ghosh",
"Paulo Tabuada",
"Ramesh Govindan",
"Gaurav S. Sukhatme",
"Pradipta Ghosh",
"Paulo Tabuada",
"Ramesh Govindan",
"Gaurav S. Sukhatme"
] | Persistent surveillance with aerial vehicles (drones) subject to connectivity and power constraints is a relatively uncharted domain of research. To reduce the complexity of multi-drone motion planning, most state-of-the-art solutions ignore network connectivity and assume unlimited battery power. Motivated by this and advances in optimization and constraint satisfaction techniques, we introduce a... |
Autonomous Planning for Multiple Aerial Cinematographers | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341622/ | [
"Luis-Evaristo Caraballo",
"Ángel Montes-Romero",
"José-Miguel Díaz-Báñez",
"Jesús Capitán",
"Arturo Torres-González",
"Aníbal Ollero",
"Luis-Evaristo Caraballo",
"Ángel Montes-Romero",
"José-Miguel Díaz-Báñez",
"Jesús Capitán",
"Arturo Torres-González",
"Aníbal Ollero"
] | This paper proposes a planning algorithm for autonomous media production with multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in outdoor events. Given filming tasks specified by a media Director, we formulate an optimization problem to maximize the filming time considering battery constraints. As we conjecture that the problem is NP-hard, we consider a discretization version, and propose a graph-based al... |
Multi-robot Coordination with Agent-Server Architecture for Autonomous Navigation in Partially Unknown Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341367/ | [
"Luca Bartolomei",
"Marco Karrer",
"Margarita Chli",
"Luca Bartolomei",
"Marco Karrer",
"Margarita Chli"
] | In this work, we present a system architecture to enable autonomous navigation of multiple agents across user-selected global interest points in a partially unknown environment. The system is composed of a server and a team of agents, here small aircrafts. Leveraging this architecture, computation-ally demanding tasks, such as global dense mapping and global path planning can be outsourced to a po... |
Decentralized Nonlinear MPC for Robust Cooperative Manipulation by Heterogeneous Aerial-Ground Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341023/ | [
"Nicola Lissandrini",
"Christos K. Verginis",
"Pedro Roque",
"Angelo Cenedese",
"Dimos V. Dimarogonas",
"Nicola Lissandrini",
"Christos K. Verginis",
"Pedro Roque",
"Angelo Cenedese",
"Dimos V. Dimarogonas"
] | Cooperative robotics is a trending topic nowadays as it makes possible a number of tasks that cannot be performed by individual robots, such as heavy payload transportation and agile manipulation. In this work, we address the problem of cooperative transportation by heterogeneous, manipulator- endowed robots. Specifically, we consider a generic number of robotic agents simultaneously grasping an o... |
In-flight range optimization of multicopters using multivariable extremum seeking with adaptive step size | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340762/ | [
"Xiangyu Wu",
"Mark W. Mueller",
"Xiangyu Wu",
"Mark W. Mueller"
] | Limited flight range is a common problem for multicopters. To alleviate this problem, we propose a method for finding the optimal speed and heading of a multicopter when flying a given path to achieve the longest flight range. Based on a novel multivariable extremum seeking controller with adaptive step size, the method (a) does not require any power consumption model of the vehicle, (b) can adapt... |
Semantic Trajectory Planning for Long-Distant Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Navigation in Urban Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341441/ | [
"Markus Ryll",
"John Ware",
"John Carter",
"Nick Roy",
"Markus Ryll",
"John Ware",
"John Carter",
"Nick Roy"
] | There has been a considerable amount of recent work on high-speed micro-aerial vehicle flight in unknown and unstructured environments. Generally these approaches either use active sensing or fly slowly enough to ensure a safe braking distance with the relatively short sensing range of passive sensors. The former generally requires carrying large and heavy LIDARs and the latter only allows flight ... |
Augmented Memory for Correlation Filters in Real-Time UAV Tracking | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341595/ | [
"Yiming Li",
"Changhong Fu",
"Fangqiang Ding",
"Ziyuan Huang",
"Jia Pan",
"Yiming Li",
"Changhong Fu",
"Fangqiang Ding",
"Ziyuan Huang",
"Jia Pan"
] | The outstanding computational efficiency of discriminative correlation filter (DCF) fades away with various complicated improvements. Previous appearances are also gradually forgotten due to the exponential decay of historical views in traditional appearance updating scheme of DCF framework, reducing the model's robustness. In this work, a novel tracker based on DCF framework is proposed to augmen... |
Next-Best-View planning for surface reconstruction of large-scale 3D environments with multiple UAVs | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340897/ | [
"Guillaume Hardouin",
"Julien Moras",
"Fabio Morbidi",
"Julien Marzat",
"El Mustapha Mouaddib",
"Guillaume Hardouin",
"Julien Moras",
"Fabio Morbidi",
"Julien Marzat",
"El Mustapha Mouaddib"
] | In this paper, we propose a novel cluster-based Next-Best-View path planning algorithm to simultaneously explore and inspect large-scale unknown environments with multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). In the majority of existing informative path-planning methods, a volumetric criterion is used for the exploration of unknown areas, and the presence of surfaces is only taken into account indirec... |
Towards Robust Visual Tracking for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle with Tri-Attentional Correlation Filters | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341784/ | [
"Yujie He",
"Changhong Fu",
"Fuling Lin",
"Yiming Li",
"Peng Lu",
"Yujie He",
"Changhong Fu",
"Fuling Lin",
"Yiming Li",
"Peng Lu"
] | Object tracking has been broadly applied in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) tasks in recent years. However, existing algorithms still face difficulties such as partial occlusion, clutter background, and other challenging visual factors. Inspired by the cutting-edge attention mechanisms, a novel object tracking framework is proposed to leverage multi-level visual attention. Three primary attention, i... |
Inspection-on-the-fly using Hybrid Physical Interaction Control for Aerial Manipulators | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341397/ | [
"Abbaraju Praveen",
"Xin Ma",
"Harikrishnan Manoj",
"Vishnunandan LN. Venkatesh",
"Mo Rastgaar",
"Richard M. Voyles",
"Abbaraju Praveen",
"Xin Ma",
"Harikrishnan Manoj",
"Vishnunandan LN. Venkatesh",
"Mo Rastgaar",
"Richard M. Voyles"
] | Inspection for structural properties (surface stiffness and coefficient of restitution) is crucial for understanding and performing aerial manipulations in unknown environments, with little to no prior knowledge on their state. Inspection-on-the-fly is the uncanny ability of humans to infer states during manipulation, reducing the necessity to perform inspection and manipulation separately. This p... |
DR2Track: Towards Real-Time Visual Tracking for UAV via Distractor Repressed Dynamic Regression | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341761/ | [
"Changhong Fu",
"Fangqiang Ding",
"Yiming Li",
"Jin Jin",
"Chen Feng",
"Changhong Fu",
"Fangqiang Ding",
"Yiming Li",
"Jin Jin",
"Chen Feng"
] | Visual tracking has yielded promising applications with unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). In literature, the advanced discriminative correlation filter (DCF) type trackers generally distinguish the foreground from the background with a learned regressor which regresses the implicit circulated samples into a fixed target label. However, the predefined and unchanged regression target results in low rob... |
Towards Vision-Based Impedance Control for the Contact Inspection of Unknown Generically-Shaped Surfaces with a Fully-Actuated UAV | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341203/ | [
"Ramy Rashad",
"Davide Bicego",
"Ran Jiao",
"Santiago Sanchez-Escalonilla",
"Stefano Stramigioli",
"Ramy Rashad",
"Davide Bicego",
"Ran Jiao",
"Santiago Sanchez-Escalonilla",
"Stefano Stramigioli"
] | The integration of computer vision techniques for the accomplishment of autonomous interaction tasks represents a challenging research direction in the context of aerial robotics. In this paper, we consider the problem of contact-based inspection of a textured target of unknown geometry and pose. Exploiting state of the art techniques in computer graphics, tuned and improved for the task at hand, ... |
Towards Deep Learning Assisted Autonomous UAVs for Manipulation Tasks in GPS-Denied Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341802/ | [
"Ashish Kumar",
"Mohit Vohra",
"Ravi Prakash",
"L. Behera",
"Ashish Kumar",
"Mohit Vohra",
"Ravi Prakash",
"L. Behera"
] | In this work, we present a pragmatic approach to enable unmanned aerial vehicle (UAVs) to autonomously perform highly complicated tasks of object pick and place. This paper is largely inspired by challenge-2 of MBZIRC 2020 and is primarily focused on the task of assembling large 3D structures in outdoors and GPS-denied environments. Primary contributions of this system are: (i) a novel computation... |
Reconstruction of 3D flight trajectories from ad-hoc camera networks | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341479/ | [
"Jingtong Li",
"Jesse Murray",
"Dorina Ismaili",
"Konrad Schindler",
"Cenek Albl",
"Jingtong Li",
"Jesse Murray",
"Dorina Ismaili",
"Konrad Schindler",
"Cenek Albl"
] | We present a method to reconstruct the 3D trajectory of an airborne robotic system only from videos recorded with cameras that are unsynchronized, may feature rolling shutter distortion, and whose viewpoints are unknown. Our approach enables robust and accurate outside-in tracking of dynamically flying targets, with cheap and easy-to-deploy equipment. We show that, in spite of the weakly constrain... |
Bayesian Fusion of Unlabeled Vision and RF Data for Aerial Tracking of Ground Targets | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341410/ | [
"Ramya Kanlapuli Rajasekaran",
"Nisar Ahmed",
"Eric Frew",
"Ramya Kanlapuli Rajasekaran",
"Nisar Ahmed",
"Eric Frew"
] | This paper presents a method for target localization and tracking in clutter using Bayesian fusion of vision and Radio Frequency (RF) sensors used aboard a small Unmanned Aircraft System (sUAS). Sensor fusion is used to ensure tracking robustness and reliability in case of camera occlusion or RF signal interference. Camera data is processed using an off-the-shelf algorithm that detects possible ob... |
Learning Visuomotor Policies for Aerial Navigation Using Cross-Modal Representations | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341049/ | [
"Rogerio Bonatti",
"Ratnesh Madaan",
"Vibhav Vineet",
"Sebastian Scherer",
"Ashish Kapoor",
"Rogerio Bonatti",
"Ratnesh Madaan",
"Vibhav Vineet",
"Sebastian Scherer",
"Ashish Kapoor"
] | Machines are a long way from robustly solving open-world perception-control tasks, such as first-person view (FPV) aerial navigation. While recent advances in end-to- end Machine Learning, especially Imitation Learning and Reinforcement appear promising, they are constrained by the need of large amounts of difficult-to-collect labeled real- world data. Simulated data, on the other hand, is easy to... |
Touch the Wind: Simultaneous Airflow, Drag and Interaction Sensing on a Multirotor | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341797/ | [
"Andrea Tagliabue",
"Aleix Paris",
"Suhan Kim",
"Regan Kubicek",
"Sarah Bergbreiter",
"Jonathan P. How",
"Andrea Tagliabue",
"Aleix Paris",
"Suhan Kim",
"Regan Kubicek",
"Sarah Bergbreiter",
"Jonathan P. How"
] | Disturbance estimation for Micro Aerial Vehicles (MAVs) is crucial for robustness and safety. In this paper, we use novel, bio-inspired airflow sensors to measure the airflow acting on a MAV, and we fuse this information in an Unscented Kalman filter (UKF) to simultaneously estimate the three-dimensional wind vector, the drag force, and other interaction forces (e.g. due to collisions, interaction... |
Fusing Concurrent Orthogonal Wide-aperture Sonar Images for Dense Underwater 3D Reconstruction | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340995/ | [
"John McConnell",
"John D. Martin",
"Brendan Englot",
"John McConnell",
"John D. Martin",
"Brendan Englot"
] | We propose a novel approach to handling the ambiguity in elevation angle associated with the observations of a forward looking multi-beam imaging sonar, and the challenges it poses for performing an accurate 3D reconstruction. We utilize a pair of sonars with orthogonal axes of uncertainty to independently observe the same points in the environment from two different perspectives, and associate th... |
A Scalable Framework for Robust Vehicle State Estimation with a Fusion of a Low-Cost IMU, the GNSS, Radar, a Camera and Lidar | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341419/ | [
"Yuran Liang",
"Steffen Müller",
"Daniel Schwendner",
"Daniel Rolle",
"Dieter Ganesch",
"Immanuel Schaffer",
"Yuran Liang",
"Steffen Müller",
"Daniel Schwendner",
"Daniel Rolle",
"Dieter Ganesch",
"Immanuel Schaffer"
] | Automated driving requires highly precise and robust vehicle state estimation for its environmental perception, motion planning and control functions. Using GPS and environmental sensors can compensate for the deficits of the estimation based on traditional vehicle dynamics sensors. However, each type of sensor has specific strengths and limitations in accuracy and robustness due to their differen... |
Vision Only 3-D Shape Estimation for Autonomous Driving | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341631/ | [
"Josephine Monica",
"Mark Campbell",
"Josephine Monica",
"Mark Campbell"
] | We present a probabilistic framework for detailed 3-D shape estimation and tracking using only vision measurements. Vision detections are processed via a bird's eye view representation, creating accurate detections at far ranges. A probabilistic model of the vision based point cloud measurements is learned and used in the framework. A 3-D shape model is developed by fusing a set of point cloud det... |
Active Alignment Control-based LED Communication for Underwater Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341442/ | [
"Pratap Bhanu Solanki",
"Shaunak D. Bopardikar",
"Xiaobo Tan",
"Pratap Bhanu Solanki",
"Shaunak D. Bopardikar",
"Xiaobo Tan"
] | Achieving and maintaining line-of-sight (LOS) is challenging for underwater optical communication systems, especially when the underlying platforms are mobile. In this work, we propose and demonstrate an active alignment controlbased LED-communication system that uses the DC value of the communication signal as feedback for LOS maintenance. Utilizing the uni-modal nature of the dependence of the l... |
An Electrocommunication System Using FSK Modulation and Deep Learning Based Demodulation for Underwater Robots | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341253/ | [
"Qinghao Wang",
"Ruijun Liu",
"Wei Wang",
"Guangming Xie",
"Qinghao Wang",
"Ruijun Liu",
"Wei Wang",
"Guangming Xie"
] | Underwater communication is extremely challenging for small underwater robots which typically have stringent power and size constraints. In our previous work, we developed an artificial electrocommunication system which could be an alternative for the communication of small underwater robots. This paper further presents a new electrocommunication system that utilizes Binary Frequency Shift Keying ... |
Demonstration of a Novel Phase Lag Controlled Roll Rotation Mechanism using a Two-DOF Soft Swimming Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341650/ | [
"Bangyuan Liu",
"Frank L. Hammond",
"Bangyuan Liu",
"Frank L. Hammond"
] | Underwater roll rotation is a basic but essential maneuver that allows many biological swimmers to achieve high maneuverability and complex locomotion patterns. In particular, sea mammals (e.g., sea otter) with flexible vertebra structures have a unique mechanism to efficiently achieve roll rotation, not propelled mainly by inter-digital webbing or fin, but by bending and twisting their body.In th... |
Topology-Aware Self-Organizing Maps for Robotic Information Gathering | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341040/ | [
"Seth McCammon",
"Dylan Jones",
"Geoffrey A. Hollinger",
"Seth McCammon",
"Dylan Jones",
"Geoffrey A. Hollinger"
] | In this paper, we present a novel algorithm for constructing a maximally informative path for a robot in an information gathering task. We use a Self-Organizing Map (SOM) framework to discover important topological features in the information function. Using these features, we identify a set of distinct classes of trajectories, each of which has improved convexity compared with the original functi... |
The SPIR: An Autonomous Underwater Robot for Bridge Pile Cleaning and Condition Assessment | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341687/ | [
"Khoa Le",
"Andrew To",
"Brenton Leighton",
"Mahdi Hassan",
"Dikai Liu",
"Khoa Le",
"Andrew To",
"Brenton Leighton",
"Mahdi Hassan",
"Dikai Liu"
] | The SPIR, Submersible Pylon Inspection Robot, is developed to provide an innovative and practical solution to keep workers safe during maintenance of underwater structures in shallow waters, which involves working in dangerous water currents, and high-pressure water-jet cleaning. More advanced than work-class Remotely Operated Vehicles technology, the SPIR is automated and required minimum involve... |
Roboat II: A Novel Autonomous Surface Vessel for Urban Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340712/ | [
"Wei Wang",
"Tixiao Shan",
"Pietro Leoni",
"David Fernández-Gutiérrez",
"Drew Meyers",
"Carlo Ratti",
"Daniela Rus",
"Wei Wang",
"Tixiao Shan",
"Pietro Leoni",
"David Fernández-Gutiérrez",
"Drew Meyers",
"Carlo Ratti",
"Daniela Rus"
] | This paper presents a novel autonomous surface vessel (ASV), called Roboat II for urban transportation. Roboat II is capable of accurate simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), receding horizon tracking control and estimation, and path planning. Roboat II is designed to maximize the internal space for transport, and can carry payloads several times of its own weight. Moreover, it is capable ... |
A Two-stage Automatic Latching System for The USVs Charging in Disturbed Berth | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341091/ | [
"Kaiwen Xue",
"Chongfeng Liu",
"Hengli Liu",
"Ruoyu Xu",
"Zhenglong Sun",
"Tin Lun Lam",
"Huihuan Qian",
"Kaiwen Xue",
"Chongfeng Liu",
"Hengli Liu",
"Ruoyu Xu",
"Zhenglong Sun",
"Tin Lun Lam",
"Huihuan Qian"
] | Automatic latching for charging in a disturbed environment for Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USVs) is always a challenging problem. In this paper, we propose a two-stage automatic latching system for USVs charging in berth. In Stage I, a vision-guided algorithm is developed to calculate an optimal latching position for charging. In Stage II, a novel latching mechanism is designed to compensate the mov... |
Variable Pitch System for the Underwater Explorer Robot UX-1 | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341759/ | [
"Ramon A. Suarez Fernandez",
"Davide Grande",
"Luca Bascetta",
"Alfredo Martins",
"Sergio Dominguez",
"Claudio Rossi",
"Ramon A. Suarez Fernandez",
"Davide Grande",
"Luca Bascetta",
"Alfredo Martins",
"Sergio Dominguez",
"Claudio Rossi"
] | This paper presents the results of the experimental tests performed to validate the functionality of a variable pitch system (VPS), designed for pitch attitude control of the novel underwater robotic vehicle explorer UX-1. The VPS is composed of a mass suspended from a central rod mounted across the hull. This mass is rotated around the transverse axis of the vehicle in order to perform a change i... |
Design and Experiments with LoCO AUV: A Low Cost Open-Source Autonomous Underwater Vehicle | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341007/ | [
"Chelsey Edge",
"Sadman Sakib Enan",
"Michael Fulton",
"Jungseok Hong",
"Jiawei Mo",
"Kimberly Barthelemy",
"Hunter Bashaw",
"Berik Kallevig",
"Corey Knutson",
"Kevin Orpen",
"Junaed Sattar",
"Chelsey Edge",
"Sadman Sakib Enan",
"Michael Fulton",
"Jungseok Hong",
"Jiawei Mo",
"Kimberly Barthelemy",
"Hunter Bashaw",
"Berik Kallevig",
"Corey Knutson",
"Kevin Orpen",
"Junaed Sattar"
] | In this paper we present the LoCO AUV, a Low-Cost, Open Autonomous Underwater Vehicle. LoCO is a general-purpose, single-person-deployable, vision-guided AUV, rated to a depth of 100 meters. We discuss the open and expandable design of this underwater robot, as well as the design of a simulator in Gazebo. Additionally, we explore the platform's preliminary local motion control and state estimation... |
Semantic Segmentation of Underwater Imagery: Dataset and Benchmark | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340821/ | [
"Md Jahidul Islam",
"Chelsey Edge",
"Yuyang Xiao",
"Peigen Luo",
"Muntaqim Mehtaz",
"Christopher Morse",
"Sadman Sakib Enan",
"Junaed Sattar",
"Md Jahidul Islam",
"Chelsey Edge",
"Yuyang Xiao",
"Peigen Luo",
"Muntaqim Mehtaz",
"Christopher Morse",
"Sadman Sakib Enan",
"Junaed Sattar"
] | In this paper, we present the first large-scale dataset for semantic Segmentation of Underwater IMagery (SUIM). It contains over 1500 images with pixel annotations for eight object categories: fish (vertebrates), reefs (invertebrates), aquatic plants, wrecks/ruins, human divers, robots, and sea-floor. The images have been rigorously collected during oceanic explorations and human-robot collaborati... |
DeepURL: Deep Pose Estimation Framework for Underwater Relative Localization | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341201/ | [
"Bharat Joshi",
"Md Modasshir",
"Travis Manderson",
"Hunter Damron",
"Marios Xanthidis",
"Alberto Quattrini Li",
"Ioannis Rekleitis",
"Gregory Dudek",
"Bharat Joshi",
"Md Modasshir",
"Travis Manderson",
"Hunter Damron",
"Marios Xanthidis",
"Alberto Quattrini Li",
"Ioannis Rekleitis",
"Gregory Dudek"
] | In this paper, we propose a real-time deep learning approach for determining the 6D relative pose of Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUV) from a single image. A team of autonomous robots localizing themselves in a communication-constrained underwater environment is essential for many applications such as underwater exploration, mapping, multi-robot convoying, and other multi-robot tasks. Due to th... |
Underwater Monocular Image Depth Estimation using Single-beam Echosounder | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340919/ | [
"Monika Roznere",
"Alberto Quattrini Li",
"Monika Roznere",
"Alberto Quattrini Li"
] | This paper proposes a methodology for real-time depth estimation of underwater monocular camera images, fusing measurements from a single-beam echosounder. Our system exploits the echosounder's detection cone to match its measurements with the detected feature points from a monocular SLAM system. Such measurements are integrated in a monocular SLAM system to adjust the visible map points and the s... |
Risk Vector-based Near miss Obstacle Avoidance for Autonomous Surface Vehicles | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341105/ | [
"Mingi Jeong",
"Alberto Quattrini Li",
"Mingi Jeong",
"Alberto Quattrini Li"
] | This paper presents a novel risk vector-based near miss prediction and obstacle avoidance method. The proposed method uses the sensor readings about the pose of the other obstacles to infer their motion model (velocity and heading) and, accordingly, adapt the risk assessment and take corrective actions if necessary. Relative vector calculations allow the method to perform in real-time. The algorit... |
Model Identification of a Small Omnidirectional Aquatic Surface Vehicle: a Practical Implementation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341142/ | [
"Keir Groves",
"Marin Dimitrov",
"Harriet Peel",
"Ognjen Marjanovic",
"Barry Lennox",
"Keir Groves",
"Marin Dimitrov",
"Harriet Peel",
"Ognjen Marjanovic",
"Barry Lennox"
] | This work presents a practical method of obtaining a dynamic system model for small omnidirectional aquatic vehicles. The models produced can be used to improve vehicle localisation, aid in the design or tuning of control systems and facilitate the development of simulated environments. The use of a dynamic model for onboard real-time velocity prediction is of particular importance for aquatic veh... |
Towards Micro Robot Hydrobatics: Vision-based Guidance, Navigation, and Control for Agile Underwater Vehicles in Confined Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341051/ | [
"Daniel A Duecker",
"Nathalie Bauschmann",
"Tim Hansen",
"Edwin Kreuzer",
"Robert Seifried",
"Daniel A Duecker",
"Nathalie Bauschmann",
"Tim Hansen",
"Edwin Kreuzer",
"Robert Seifried"
] | Despite the recent progress, guidance, navigation, and control (GNC) are largely unsolved for agile micro autonomous underwater vehicles (μAUVs). Hereby, robust and accurate self-localization systems which fit μAUVs play a key role and their absence constitutes a severe bottleneck in micro underwater robotics research. In this work we present, first, a small-size low-cost high performance vision-b... |
On Parameter Estimation of Flexible Space Manipulator Systems | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340768/ | [
"Olga-Orsalia Christidi-Loumpasefski",
"Kostas Nanos",
"Evangelos Papadopoulos",
"Olga-Orsalia Christidi-Loumpasefski",
"Kostas Nanos",
"Evangelos Papadopoulos"
] | Space manipulator systems in orbit are subject to link flexibilities since they are designed to be lightweight and long reaching. Often, their joints are driven by harmonic gear-motor units, which introduce joint flexibility. Both of these types of flexibility may cause structural vibrations. To improve endpoint tracking, advanced control strategies that benefit from the knowledge of system parame... |
Comparison between Stationary and Crawling Multi-Arm Robotics for In-Space Assembly | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341141/ | [
"Katherine McBryan",
"Katherine McBryan"
] | In-space assembly (ISA) is the next step to building larger and more permanent structures in orbit. The use of a robotic in-space assembler saves on costly and potentially risky EVAs. Determining the best robot for ISA is difficult as it will depend on the structure being assembled. A comparison between two categories of robots is presented: a stationary robot and robot which crawls along the trus... |
Interactive Planning and Supervised Execution for High-Risk, High-Latency Teleoperation | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340800/ | [
"Will Pryor",
"Balazs P. Vagvolgyi",
"Anton Deguet",
"Simon Leonard",
"Louis L. Whitcomb",
"Peter Kazanzides",
"Will Pryor",
"Balazs P. Vagvolgyi",
"Anton Deguet",
"Simon Leonard",
"Louis L. Whitcomb",
"Peter Kazanzides"
] | Ground-based teleoperation of robot manipulators for on-orbit servicing of spacecraft represents an example of high-payoff, high-risk operations that are challenging to perform due to high latency communications, with telemetry time delays of several seconds. In these scenarios, confidence of operating without failure is paramount. We report the development of an Interactive Planning and Supervise... |
Parameter Identification for an Uncooperative Captured Satellite with Spinning Reaction Wheels | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341749/ | [
"Olga-Orsalia Christidi-Loumpasefski",
"Evangelos Papadopoulos",
"Olga-Orsalia Christidi-Loumpasefski",
"Evangelos Papadopoulos"
] | A novel identification method is developed which identifies the accumulated angular momentum (AAM) of spinning reaction wheels (RWs) of an uncooperative satellite captured by a robotic servicer. In contrast to other methods that treat captured satellite's RWs as non-spinning, the developed method provides simultaneously accurate estimates of the AAM of the captured satellite's RWs and of the inert... |
Tumbling and Hopping Locomotion Control for a Minor Body Exploration Robot | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341223/ | [
"Keita Kobashi",
"Ayumu Bando",
"Kenji Nagaoka",
"Kazuya Yoshida",
"Keita Kobashi",
"Ayumu Bando",
"Kenji Nagaoka",
"Kazuya Yoshida"
] | This paper presents the modeling and analysis of a novel moving mechanism "tumbling" for asteroid exploration. The system actuation is provided by an internal motor and torque wheel; elastic spring-mounted spikes are attached to the perimeter of a circular-shaped robot, protruding normal to the surface and distributed uniformly. Compared with the conventional motion mechanisms, this simple layout ... |
Inertia-Decoupled Equations for Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation of an Orbital Robot with External Forces | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341633/ | [
"Hrishik Mishra",
"Alessandro M. Giordano",
"Marco De Stefano",
"Roberto Lampariello",
"Christian Ott",
"Hrishik Mishra",
"Alessandro M. Giordano",
"Marco De Stefano",
"Roberto Lampariello",
"Christian Ott"
] | In this paper, we propose three novel Hardware-in-the-loop simulation (HLS) methods for a fully-actuated orbital robot in the presence of external interactions using On-Ground Facility Manipulators (OGFM). In particular, a fixed-base and a vehicle-driven manipulator are considered in the analyses. The key idea is to describe the orbital robot's dynamics using the Lagrange-Poincaré(LP) equations, w... |
A Target Tracking and Positioning Framework for Video Satellites Based on SLAM | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341270/ | [
"Xuhui Zhao",
"Zhi Gao",
"Yongjun Zhang",
"Ben M. Chen",
"Xuhui Zhao",
"Zhi Gao",
"Yongjun Zhang",
"Ben M. Chen"
] | With the booming development in aerospace technology, the video satellite which observes the live phenomena on the ground by video shooting has gradually emerged as a new Earth observation method. And remote sensing comes into a "dynamic" era with the demand for new processing techniques, especially the near-real-time tracking and geo-positioning algorithm for ground moving targets. However, many ... |
Gaussian Process Gradient Maps for Loop-Closure Detection in Unstructured Planetary Environments | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341667/ | [
"Cedric Le Gentil",
"Mallikarjuna Vayugundla",
"Riccardo Giubilato",
"Wolfgang Stürzl",
"Teresa Vidal-Calleja",
"Rudolph Triebel",
"Cedric Le Gentil",
"Mallikarjuna Vayugundla",
"Riccardo Giubilato",
"Wolfgang Stürzl",
"Teresa Vidal-Calleja",
"Rudolph Triebel"
] | The ability to recognize previously mapped locations is an essential feature for autonomous systems. Unstructured planetary-like environments pose a major challenge to these systems due to the similarity of the terrain. As a result, the ambiguity of the visual appearance makes state-of-the-art visual place recognition approaches less effective than in urban or man-made environments. This paper pre... |
Visual Monitoring and Servoing of a Cutting Blade during Telerobotic Satellite Servicing | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341485/ | [
"Amama Mahmood",
"Balazs P. Vagvolgyi",
"Will Pryor",
"Louis L. Whitcomb",
"Peter Kazanzides",
"Simon Leonard",
"Amama Mahmood",
"Balazs P. Vagvolgyi",
"Will Pryor",
"Louis L. Whitcomb",
"Peter Kazanzides",
"Simon Leonard"
] | We propose a system for visually monitoring and servoing the cutting of a multi-layer insulation (MLI) blanket that covers the envelope of satellites and spacecraft. The main contributions of this paper are: 1) to propose a model for relating visual features describing the engagement depth of the blade to the force exerted on the MLI blanket by the cutting tool, 2) a blade design and algorithm to ... |
Subsurface Sampling Robot for Time-limited Asteroid Exploration | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340645/ | [
"Hiroki Kato",
"Yasutaka Satou",
"Kent Yoshikawa",
"Masatsugu Otsuki",
"Hirotaka Sawada",
"Takeshi Kuratomi",
"Nana Hidaka",
"Hiroki Kato",
"Yasutaka Satou",
"Kent Yoshikawa",
"Masatsugu Otsuki",
"Hirotaka Sawada",
"Takeshi Kuratomi",
"Nana Hidaka"
] | This paper presents a novel approach to sampling subsurface asteroidal regolith under severe time constraints. Sampling operations that must be completed within a few hours require techniques that can manage subsurface obstructions that may be encountered. The large uncertainties due to our lack of knowledge of regolith properties also make sampling difficult. To aid in managing these challenges, ... |
Robots Made From Ice: An Analysis of Manufacturing Techniques | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340855/ | [
"Devin Carroll",
"Mark Yim",
"Devin Carroll",
"Mark Yim"
] | Modular robotic systems with self-repair or self-replication capabilities have been presented as a robust, low cost solution to extraterrestrial or Arctic exploration. This paper explores using ice as the sole structure element to build robots. The ice allows for increased flexibility in the system design, enabling the robotic structure to be designed and built post deployment, after tasks and ter... |
Autonomous Navigation over Europa Analogue Terrain for an Actively Articulated Wheel-on-Limb Rover | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341234/ | [
"William Reid",
"Michael Paton",
"Sisir Karumanchi",
"Brendan Chamberlain-Simon",
"Blair Emanuel",
"Gareth Meirion-Griffith",
"William Reid",
"Michael Paton",
"Sisir Karumanchi",
"Brendan Chamberlain-Simon",
"Blair Emanuel",
"Gareth Meirion-Griffith"
] | The ocean world Europa is a prime target for exploration given its potential habitability [1]. We propose a mobile robotic system that is capable of autonomously traversing tens of meters to visit multiple sites of interest on a Europan analogue surface. Due to the topology of Europan terrain being largely unknown, it is desired that this mobility system traverse a large variety of terrain types. ... |
Autonomous Multi-Robot Assembly of Solar Array Modules: Experimental Analysis and Insights | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341298/ | [
"Holly Everson",
"Joshua Moser",
"Amy Quartaro",
"Samantha Glassner",
"Erik Komendera",
"Holly Everson",
"Joshua Moser",
"Amy Quartaro",
"Samantha Glassner",
"Erik Komendera"
] | To allow for the construction of large space structures to support future space endeavors, autonomous robotic solutions would serve to reduce cost and risk of human extravehicular activity (EVA). Practicality of autonomous assembly requires both theoretical and algorithmic advances, and hardware experimentation across a spectrum of technological readiness levels. Analysis of hardware experiments p... |
Accurate, Low-Latency Visual Perception for Autonomous Racing: Challenges, Mechanisms, and Practical Solutions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341683/ | [
"Kieran Strobel",
"Sibo Zhu",
"Raphael Chang",
"Skanda Koppula",
"Kieran Strobel",
"Sibo Zhu",
"Raphael Chang",
"Skanda Koppula"
] | Autonomous racing provides the opportunity to test safety-critical perception pipelines at their limit. This paper describes the practical challenges and solutions to applying state-of-the-art computer vision algorithms to build a low-latency, high-accuracy perception system for DUT18 Driverless (DUT18D), a 4WD electric race car with podium finishes at all Formula Driverless competitions for which... |
Spatio-Temporal Ultrasonic Dataset: Learning Driving from Spatial and Temporal Ultrasonic Cues | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340765/ | [
"Shuai Wang",
"Jiahu Qin",
"Zhanpeng Zhang",
"Shuai Wang",
"Jiahu Qin",
"Zhanpeng Zhang"
] | Recent works have proved that combining spatial and temporal visual cues can significantly improve the performance of various vision-based robotic systems. However, for the ultrasonic sensors used in most robotic tasks (e.g. collision avoidance, localization and navigation), there is a lack of benchmark ultrasonic datasets that consist of spatial and temporal data to verify the usability of spatia... |
A POMDP Treatment of Vehicle-Pedestrian Interaction: Implicit Coordination via Uncertainty-Aware Planning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341320/ | [
"Ya-Chuan Hsu",
"Swaminathan Gopalswamy",
"Srikanth Saripalli",
"Dylan A. Shell",
"Ya-Chuan Hsu",
"Swaminathan Gopalswamy",
"Srikanth Saripalli",
"Dylan A. Shell"
] | Drivers and other road users often encounter situations (e.g., arriving at an intersection simultaneously) where priority is ambiguous or unclear but must be resolved via communication to reach agreement. This poses a challenge for autonomous vehicles, for which no direct means for expressing intent and acknowledgment has yet been established. This paper contributes a minimal model to manage ambig... |
Multiple Trajectory Prediction with Deep Temporal and Spatial Convolutional Neural Networks | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341327/ | [
"Jan Strohbeck",
"Vasileios Belagiannis",
"Johannes Müller",
"Marcel Schreiber",
"Martin Herrmann",
"Daniel Wolf",
"Michael Buchholz",
"Jan Strohbeck",
"Vasileios Belagiannis",
"Johannes Müller",
"Marcel Schreiber",
"Martin Herrmann",
"Daniel Wolf",
"Michael Buchholz"
] | Automated vehicles need to not only perceive their environment, but also predict the possible future behavior of all detected traffic participants in order to safely navigate in complex scenarios and avoid critical situations, ranging from merging on highways to crossing urban intersections. Due to the availability of datasets with large numbers of recorded trajectories of traffic participants, de... |
End-to-end Autonomous Driving Perception with Sequential Latent Representation Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341020/ | [
"Jianyu Chen",
"Zhuo Xu",
"Masayoshi Tomizuka",
"Jianyu Chen",
"Zhuo Xu",
"Masayoshi Tomizuka"
] | Current autonomous driving systems are composed of a perception system and a decision system. Both of them are divided into multiple subsystems built up with lots of human heuristics. An end-to-end approach might clean up the system and avoid huge efforts of human engineering, as well as obtain better performance with increasing data and computation resources. Compared to the decision system, the ... |
PillarFlow: End-to-end Birds-eye-view Flow Estimation for Autonomous Driving | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340931/ | [
"Kuan-Hui Lee",
"Matthew Kliemann",
"Adrien Gaidon",
"Jie Li",
"Chao Fang",
"Sudeep Pillai",
"Wolfram Burgard",
"Kuan-Hui Lee",
"Matthew Kliemann",
"Adrien Gaidon",
"Jie Li",
"Chao Fang",
"Sudeep Pillai",
"Wolfram Burgard"
] | In autonomous driving, accurately estimating the state of surrounding obstacles is critical for safe and robust path planning. However, this perception task is difficult, particularly for generic obstacles/objects, due to appearance and occlusion changes. To tackle this problem, we propose an end-to-end deep learning framework for LIDAR-based flow estimation in bird's eye view (BeV). Our method ta... |
Real-time Detection of Distracted Driving using Dual Cameras | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340921/ | [
"Duy Tran",
"Ha Manh Do",
"Jiaxing Lu",
"Weihua Sheng",
"Duy Tran",
"Ha Manh Do",
"Jiaxing Lu",
"Weihua Sheng"
] | Distracted driving is one of the main contributors to traffic accidents. This paper proposes a deep learning approach to detecting multiple distracted driving behaviors. In order to obtain more accurate detection results, a synchronized image recognition system based on two cameras is designed, by which the body movements and face of the driver are monitored respectively. The images captured from ... |
Expressing Diverse Human Driving Behavior with Probabilistic Rewards and Online Inference | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341371/ | [
"Liting Sun",
"Zheng Wu",
"Hengbo Ma",
"Masayoshi Tomizuka",
"Liting Sun",
"Zheng Wu",
"Hengbo Ma",
"Masayoshi Tomizuka"
] | In human-robot interaction (HRI) systems, such as autonomous vehicles, understanding and representing human behavior are important. Human behavior is naturally rich and diverse. Cost/reward learning, as an efficient way to learn and represent human behavior, has been successfully applied in many domains. Most of traditional inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) algorithms, however, cannot adequatel... |
Identification of Effective Motion Primitives for Ground Vehicles | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341708/ | [
"Tobias Löw",
"Tirthankar Bandyopadhyay",
"Paulo V. K. Borges",
"Tobias Löw",
"Tirthankar Bandyopadhyay",
"Paulo V. K. Borges"
] | Understanding the kinematics of a ground robot is essential for efficient navigation. Based on the kinematic model of a robot, its full motion capabilities can be represented by theoretical motion primitives. However, depending on the environment and/or human preferences, not all of those theoretical motion primitives are desirable and/or achievable. This work presents a method to identify effecti... |
CMetric: A Driving Behavior Measure using Centrality Functions | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341720/ | [
"Rohan Chandra",
"Uttaran Bhattacharya",
"Trisha Mittal",
"Aniket Bera",
"Dinesh Manocha",
"Rohan Chandra",
"Uttaran Bhattacharya",
"Trisha Mittal",
"Aniket Bera",
"Dinesh Manocha"
] | We present a new measure, CMetric, to classify driver behaviors using centrality functions. Our formulation combines concepts from computational graph theory and social traffic psychology to quantify and classify the behavior of human drivers. CMetric is used to compute the probability of a vehicle executing a driving style, as well as the intensity used to execute the style. Our approach is desig... |
Frontier Detection and Reachability Analysis for Efficient 2D Graph-SLAM Based Active Exploration | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341735/ | [
"Zezhou Sun",
"Banghe Wu",
"Cheng-Zhong Xu",
"Sanjay E. Sarma",
"Jian Yang",
"Hui Kong",
"Zezhou Sun",
"Banghe Wu",
"Cheng-Zhong Xu",
"Sanjay E. Sarma",
"Jian Yang",
"Hui Kong"
] | We propose an integrated approach to active exploration by exploiting the Cartographer method as the base SLAM module for submap creation and performing efficient frontier detection in the geometrically co-aligned submaps induced by graph optimization. We also carry out analysis on the reachability of frontiers and their clusters to ensure that the detected frontier can be reached by robot. Our me... |
Probabilistic Semantic Mapping for Urban Autonomous Driving Applications | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341738/ | [
"David Paz",
"Hengyuan Zhang",
"Qinru Li",
"Hao Xiang",
"Henrik I. Christensen",
"David Paz",
"Hengyuan Zhang",
"Qinru Li",
"Hao Xiang",
"Henrik I. Christensen"
] | Recent advancements in statistical learning and computational abilities have enabled autonomous vehicle technology to develop at a much faster rate. While many of the architectures previously introduced are capable of operating under highly dynamic environments, many of these are constrained to smaller-scale deployments, require constant maintenance due to the associated scalability cost with high... |
City-Scale Grid-Topological Hybrid Maps for Autonomous Mobile Robot Navigation in Urban Area | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340990/ | [
"Shun Niijima",
"Ryusuke Umeyama",
"Yoko Sasaki",
"Hiroshi Mizoguchi",
"Shun Niijima",
"Ryusuke Umeyama",
"Yoko Sasaki",
"Hiroshi Mizoguchi"
] | Extensive city navigation remains an unresolved problem for autonomous mobile robots that share space with pedestrians. This paper proposes a configuration for a navigation map that expresses urban structures and an autonomous navigation scheme that uses the configuration. The proposed map configuration is a hybrid structure of multiple 2D grid maps and a topological graph. The occupancy grids for... |
SCALE-Net: Scalable Vehicle Trajectory Prediction Network under Random Number of Interacting Vehicles via Edge-enhanced Graph Convolutional Neural Network | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341288/ | [
"Hyeongseok Jeon",
"Junwon Choi",
"Dongsuk Kum",
"Hyeongseok Jeon",
"Junwon Choi",
"Dongsuk Kum"
] | Predicting the future trajectory of surrounding vehicles in a randomly varying traffic level is one of the most challenging problems in developing an autonomous vehicle. Since there is no pre-defined number of interacting vehicles participated in, the prediction network has to be scalable with respect to the number of vehicles in order to guarantee consistent performance in terms of both accuracy ... |
Behaviorally Diverse Traffic Simulation via Reinforcement Learning | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341493/ | [
"Shinya Shiroshita",
"Shirou Maruyama",
"Daisuke Nishiyama",
"Mario Ynocente Castro",
"Karim Hamzaoui",
"Guy Rosman",
"Jonathan DeCastro",
"Kuan-Hui Lee",
"Adrien Gaidon",
"Shinya Shiroshita",
"Shirou Maruyama",
"Daisuke Nishiyama",
"Mario Ynocente Castro",
"Karim Hamzaoui",
"Guy Rosman",
"Jonathan DeCastro",
"Kuan-Hui Lee",
"Adrien Gaidon"
] | Traffic simulators are important tools in autonomous driving development. While continuous progress has been made to provide developers more options for modeling various traffic participants, tuning these models to increase their behavioral diversity while maintaining quality is often very challenging. This paper introduces an easily-tunable policy generation algorithm for autonomous driving agent... |
Predictive Runtime Monitoring of Vehicle Models Using Bayesian Estimation and Reachability Analysis | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340755/ | [
"Yi Chou",
"Hansol Yoon",
"Sriram Sankaranarayanan",
"Yi Chou",
"Hansol Yoon",
"Sriram Sankaranarayanan"
] | We present a predictive runtime monitoring technique for estimating future vehicle positions and the probability of collisions with obstacles. Vehicle dynamics model how the position and velocity change over time as a function of external inputs. They are commonly described by discrete-time stochastic models. Whereas positions and velocities can be measured, the inputs (steering and throttle) are ... |
Task-Motion Planning for Safe and Efficient Urban Driving | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341522/ | [
"Yan Ding",
"Xiaohan Zhang",
"Xingyue Zhan",
"Shiqi Zhang",
"Yan Ding",
"Xiaohan Zhang",
"Xingyue Zhan",
"Shiqi Zhang"
] | Autonomous vehicles need to plan at the task level to compute a sequence of symbolic actions, such as merging left and turning right, to fulfill people's service requests, where efficiency is the main concern. At the same time, the vehicles must compute continuous trajectories to perform actions at the motion level, where safety is the most important. Task-motion planning in autonomous driving fac... |
Feedback Enhanced Motion Planning for Autonomous Vehicles | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340951/ | [
"Ke Sun",
"Brent Schlotfeldt",
"Stephen Chaves",
"Paul Martin",
"Gulshan Mandhyan",
"Vijay Kumar",
"Ke Sun",
"Brent Schlotfeldt",
"Stephen Chaves",
"Paul Martin",
"Gulshan Mandhyan",
"Vijay Kumar"
] | In this work, we address the motion planning problem for autonomous vehicles through a new lattice planning approach, called Feedback Enhanced Lattice Planner (FELP). Existing lattice planners have two major limitations, namely the high dimensionality of the lattice and the lack of modeling of agent vehicle behaviors. We propose to apply the Intelligent Driver Model (IDM) [1] as a speed feedback p... |
GndNet: Fast Ground Plane Estimation and Point Cloud Segmentation for Autonomous Vehicles | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9340979/ | [
"Anshul Paigwar",
"Özgür Erkent",
"David Sierra-Gonzalez",
"Christian Laugier",
"Anshul Paigwar",
"Özgür Erkent",
"David Sierra-Gonzalez",
"Christian Laugier"
] | Ground plane estimation and ground point segmentation is a crucial precursor for many applications in robotics and intelligent vehicles like navigable space detection and occupancy grid generation, 3D object detection, point cloud matching for localization and registration for mapping. In this paper, we present GndNet, a novel end-to-end approach that estimates the ground plane elevation informati... |
Intelligent Exploration and Autonomous Navigation in Confined Spaces | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341525/ | [
"Aliakbar Akbari",
"Puneet S Chhabra",
"Ujjar Bhandari",
"Sara Bernardini",
"Aliakbar Akbari",
"Puneet S Chhabra",
"Ujjar Bhandari",
"Sara Bernardini"
] | Autonomous navigation and exploration in confined spaces are currently setting new challenges for robots. The presence of narrow passages, flammable atmosphere, dust, smoke, and other hazards makes the mapping and navigation tasks extremely difficult. To tackle these challenges, robots need to make intelligent decisions, maximising information while maintaining the safety of the system and their s... |
IROS 2020 Accepted Paper Meta Info Dataset
This dataset is collect from the IROS 2020-2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/conhome/1000393/all-proceedings) as well as the arxiv website DeepNLP paper arxiv (http://www.deepnlp.org/content/paper/iros2021). For researchers who are interested in doing analysis of IROS 2020 accepted papers and potential trends, you can use the already cleaned up json files. Each row contains the meta information of a paper in the IROS 2020 conference. To explore more AI & Robotic papers (NIPS/ICML/ICLR/IROS/ICRA/etc) and AI equations, feel free to navigate the Equation Search Engine (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/equation) as well as the AI Agent Search Engine to find the deployed AI Apps and Agents (http://www.deepnlp.org/search/agent) in your domain.
Equations Latex code and Papers Search Engine
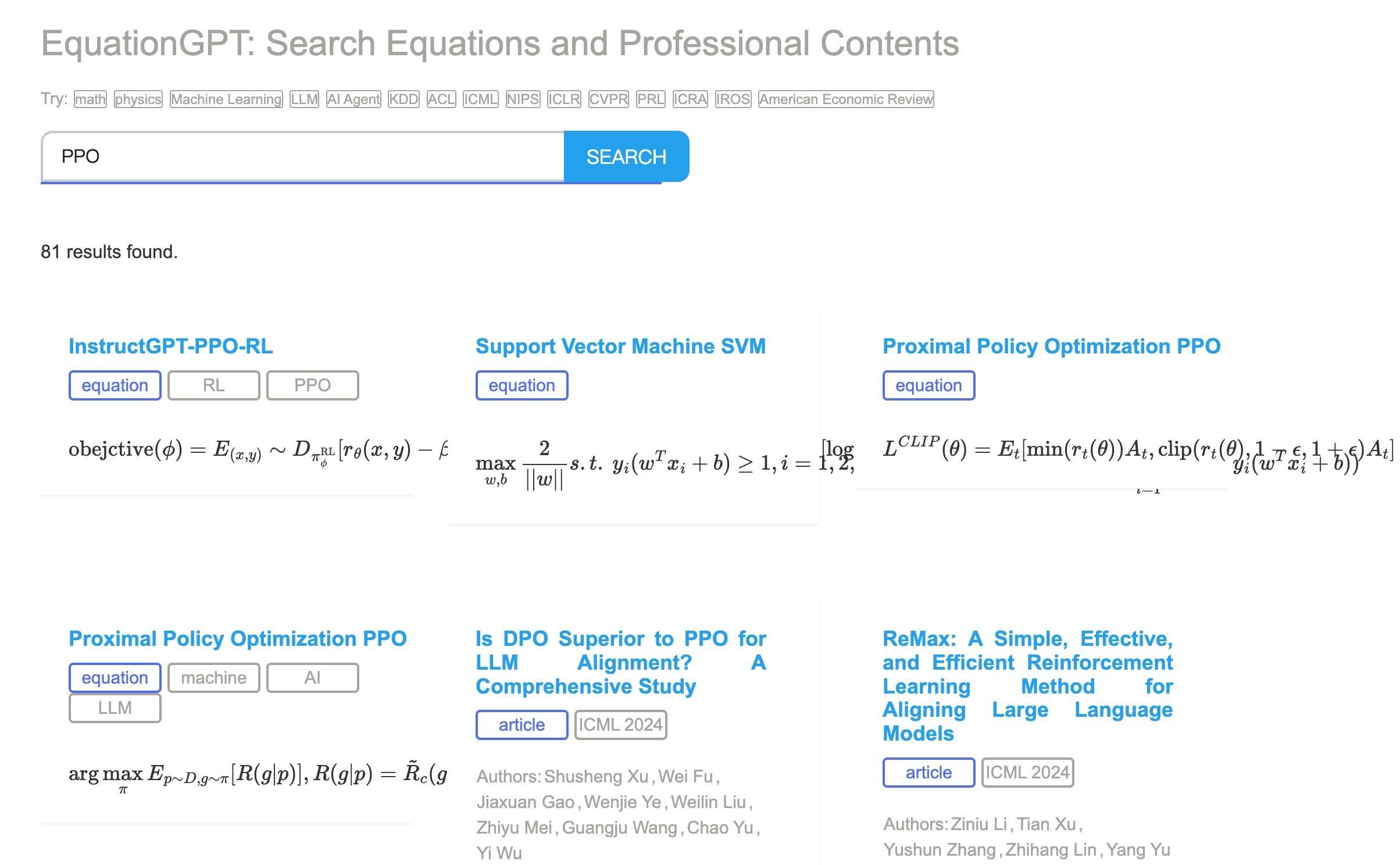
Meta Information of Json File of Paper
{
"title": "Staging energy sources to extend flight time of a multirotor UAV",
"detail_url": "https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9341804/",
"author_list": ["Karan P. Jain", "Jerry Tang", "Koushil Sreenath", "Mark W. Mueller", "Karan P. Jain", "Jerry Tang", "Koushil Sreenath", "Mark W. Mueller"],
"abstract": "Energy sources such as batteries do not decrease in mass after consumption, unlike combustion-based fuels. We present the concept of staging energy sources, i.e. consuming energy in stages and ejecting used stages, to progressively reduce the mass of aerial vehicles in-flight which reduces power consumption, and consequently increases flight time. A flight time vs. energy storage mass analysis is ..."
}
Related
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
AI Agent Marketplace and Search
Robot Search
Equation and Academic search
AI & Robot Comprehensive Search
AI & Robot Question
AI & Robot Community
AI Agent Marketplace Blog
AI Agent Reviews
AI Agent Marketplace Directory
Microsoft AI Agents Reviews
Claude AI Agents Reviews
OpenAI AI Agents Reviews
Saleforce AI Agents Reviews
AI Agent Builder Reviews
AI Equation
List of AI Equations and Latex
List of Math Equations and Latex
List of Physics Equations and Latex
List of Statistics Equations and Latex
List of Machine Learning Equations and Latex
- Downloads last month
- 51