File size: 3,075 Bytes
4b9346d fe0b8ce caa2baf fe0b8ce d4d769c 7ecd01a eb9905a 4171d41 87126d1 4171d41 f2b614f 87126d1 f2b614f d4d769c 87126d1 3e0cb79 eb9905a 5fac11f ebf91a8 5fac11f 87126d1 5fac11f 87126d1 5fac11f 87126d1 5fac11f c7e0d94 b830950 c7e0d94 eb9905a f2b614f eb9905a 1e8fc81 87126d1 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 |
---
license: mit
datasets:
- ccmusic-database/music_genre
language:
- en
metrics:
- accuracy
pipeline_tag: audio-classification
tags:
- music
- art
---
# Intro
The music genre classification model is fine-tuned based on a pre-trained model from the computer vision (CV) domain, aiming to classify audio data into different genres. During the pre-training phase, the model learns rich feature representations using a large-scale dataset from computer vision tasks. Through transfer learning, these learned features are applied to the music genre classification task to enhance the model's performance on audio data. In the fine-tuning phase, an audio dataset containing 16 music genre categories is utilized. These audio samples are first transformed into spectrograms, converting the temporal audio signal into a two-dimensional representation in the time and frequency dimensions. The spectrogram representation captures the temporal evolution of different audio frequencies, providing the model with rich information about the audio content. Through fine-tuning, adjustments are made to the pre-trained model to meet the requirements of the music genre classification task. The model learns to extract features from spectrograms that are relevant to music genre, enabling accurate classification of audio samples. This process enables the model to recognize and infer music genres, such as rock, classical, pop, among others. By combining a pre-trained model from the computer vision domain with an audio task, this approach leverages cross-modal knowledge transfer, demonstrating the adaptability and effectiveness of pre-trained models across different domains.
## Demo
<https://huggingface.co/spaces/ccmusic-database/music_genre>
## Usage
```python
from modelscope import snapshot_download
model_dir = snapshot_download("ccmusic-database/music_genre")
```
## Maintenance
```bash
git clone [email protected]:ccmusic-database/music_genre
cd music_genre
```
## Results
[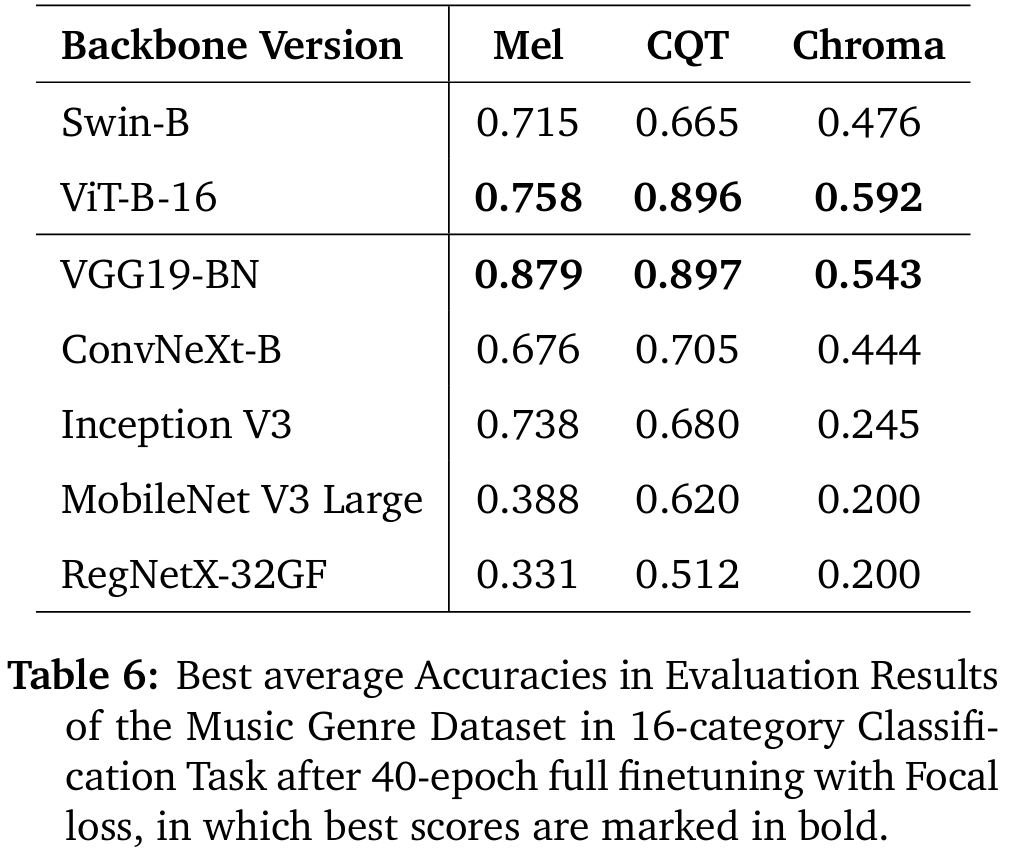](#best-result)
### Best Result
A demo result of VGG19_BN fine-tuned on CQT:
<style>
#pianos td {
vertical-align: middle !important;
text-align: center;
}
#pianos th {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<table id="pianos">
<tr>
<th>Loss curve</th>
<td><img src="https://www.modelscope.cn/models/ccmusic-database/music_genre/resolve/master/vgg19_bn_cqt/loss.jpg"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Training and validation accuracy</th>
<td><img src="https://www.modelscope.cn/models/ccmusic-database/music_genre/resolve/master/vgg19_bn_cqt/acc.jpg"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Confusion matrix</th>
<td><img src="https://www.modelscope.cn/models/ccmusic-database/music_genre/resolve/master/vgg19_bn_cqt/mat.jpg"></td>
</tr>
</table>
## Dataset
<https://huggingface.co/datasets/ccmusic-database/music_genre>
## Mirror
<https://www.modelscope.cn/models/ccmusic-database/music_genre>
## Evaluation
<https://github.com/monetjoe/ccmusic_eval> |